In our previous blog, we defined an instance action to update the Billing Date of a billing document.
If you observed the generated method in the Behavior Implementation Class, the action automatically imports a parameter called KEYS.
METHODS updatebillingdate FOR MODIFY
IMPORTING keys FOR ACTION zsac_i_bill_header~updatebillingdate
RESULT result.What does KEYS represent?
The parameter keys contains the identifying fields of the RAP BO instance on which the action is being executed.
When a user selects a billing document in the Fiori app and triggers the action, RAP passes the key of that selected record to this method.
RAP BO and RAP BO Instance
In our Billing Document app:
-
The RAP BO is the complete business object built around
the root entityzsac_i_bill_headerand its child item entity. -
A RAP BO instance is a single billing document record,
for example Billing Document 1001.
So when we click the action on one record, the framework executes the logic only for that specific RAP BO instance, and its key is delivered through the keys parameter.
So far, our action:
-
was bound to a specific instance
-
received only instance keys as input
But what if we need:
-
an action that is not linked to a single record, or
-
an action that accepts additional input parameters from the user?
This is where static actions and abstract entities as parameter structures come into the picture.
What is a static action?
A static action is a non-standard operation that can be executed independent of any RAP BO instance.
In simple terms, you can trigger the action from the UI without selecting any record. Unlike an instance action, a static action is not tied to a specific billing document.
Then what about the input?
Since no instance is involved, the action:
-
may have %CID as importing parameter
-
or can accept a custom parameter structure defined by us.
This custom parameter is typically defined using an Abstract CDS Entity.
So the overall approach becomes:
-
Create an Abstract CDS entity for parameters
-
Define the static action in BDEF
-
Implement the action logic
-
Expose it in projection
-
Expose it on the UI
Exactly the same steps as an instance action, but without dependency on KEYS.
What is an Abstract CDS Entity?
CDS abstract entities are used to define structured data types in ABAP CDS.
Key characteristics:
-
They are transient entities
-
No database table or view is generated
-
They cannot be accessed using ABAP SQL
-
They exist only as type definitions
In the context of RAP, abstract entities are mainly used as:
-
parameters for RAP actions
-
parameters for RAP functions
-
payload structures for RAP business events
This makes them perfect for scenarios where we need to pass user input to a static action.
Implementing Static Action with Abstract Entity Parameters
In our scenario, we will create a new Billing Document record using a static action by asking the user to enter:
-
Billing Document ID
-
Billing Document Type
-
Billing Date
Steps to follow
Step 1: Create an Abstract CDS Entity
Create a new Data Definition using the template
defineAbstractEntityWithParameters
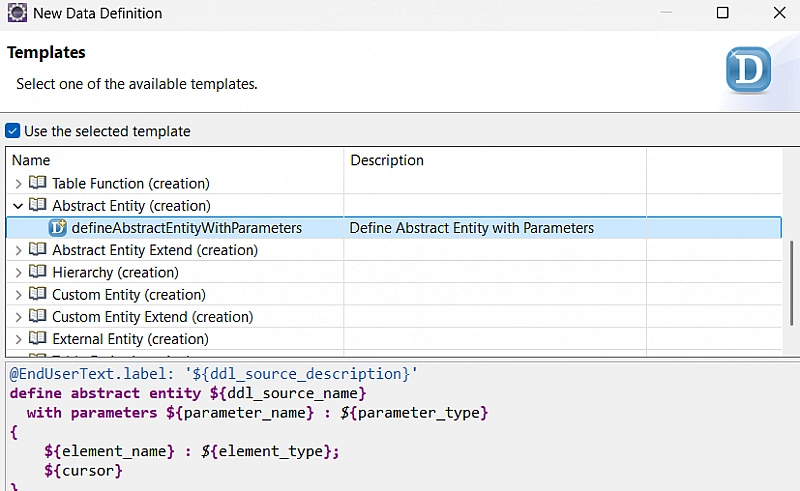
Enter the following code in the abstract entity you created:
@EndUserText.label: 'Parameters for Create Bill Header Action'
define abstract entity ZSAC_A_CREATE_BILL_PARAMS
{
@EndUserText.label: 'Billing Document ID'
BillID : abap.char(10);
@EndUserText.label: 'Billing Document Type'
BillType : abap.char(4);
@EndUserText.label: 'Billing Date'
BillDate : abap.dats;
}This abstract entity will act as the parameter structure for our static action.
Step 2: Define Static Action in Behavior Definition
Add the following static action to the behavior definition of Billing Document Header:
static action createBillingDocHeader parameter ZSAC_A_CREATE_BILL_PARAMS result [1] $self;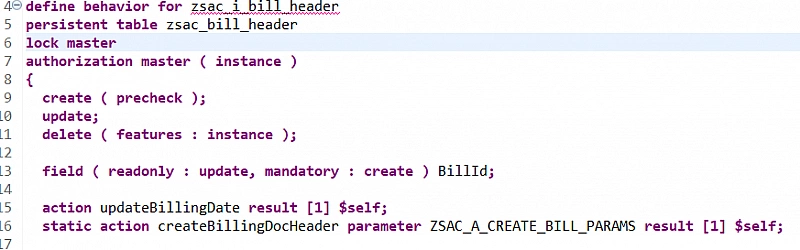
Replace
ZSAC_A_CREATE_BILL_PARAMSwith the name of your abstract entity if it is different.
Important Note
-
When a static action defines a result parameter, the framework navigates to the object page of the newly created instance.
-
If the result parameter is not specified, the new instance appears on the list page without page refresh.
-
This behavior applies to non-draft applications.
After defining the action, ADT provides a quick fix to generate the implementation method.
Step 3: Implement Static Action
Add the following logic in the generated method of the behavior implementation class.
Replace the RAP BO name with your own where required.
DATA: bill_header_create TYPE TABLE FOR CREATE zsac_i_bill_header,
bill_header_result TYPE TABLE FOR ACTION RESULT zsac_i_bill_header~createBillingDocHeader,
response_data TYPE TABLE FOR READ RESULT zsac_i_bill_header.
LOOP AT keys INTO DATA(key).
" Prepare create structure from action parameters
APPEND VALUE #( %cid = key-%cid
BillId = key-%param-BillID
BillType = key-%param-BillType
BillDate = key-%param-BillDate )
TO bill_header_create.
APPEND VALUE #( %cid = key-%cid ) TO bill_header_result.
ENDLOOP.
" Create the bill header records
MODIFY ENTITIES OF zsac_i_bill_header IN LOCAL MODE
ENTITY zsac_i_bill_header
CREATE FIELDS ( BillId BillType BillDate )
WITH bill_header_create
MAPPED DATA(mapped_create)
FAILED DATA(failed_create)
REPORTED DATA(reported_create).
" Prepare action result
result = VALUE #( FOR create IN mapped_create-zsac_i_bill_header INDEX INTO i (
%cid = create-%cid
%param-BillId = bill_header_create[ %cid = create-%cid ]-BillId
) ).This logic:
-
reads the parameters passed from UI
-
creates a new billing document
-
returns the created instance as action result
Step 4: Project the Action
Expose the static action in the Behavior Projection of zsac_i_bill_header:
use action createBillingDocHeader;Step 5: Expose the Action on UI
Add the following line in the Metadata Extension of Billing Document Header:
{ position: 20, type: #FOR_ACTION, dataAction: 'createBillingDocHeader', label: 'Create Billing Document' }
Now we have two actions on the UI:
-
Position 10 → Instance action
-
Position 20 → Static action
Test the application
Activate the metadata extension and open the app.
You will notice that the static action is enabled even without selecting any record.
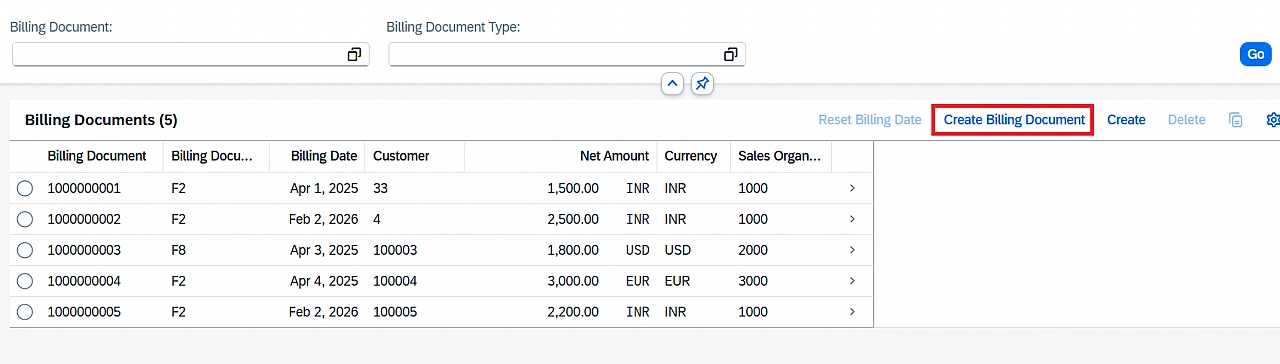
Clicking the action opens a popup dialog based on the abstract entity.
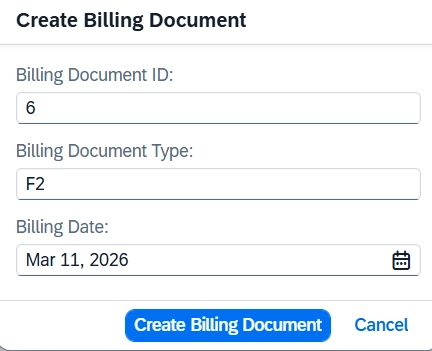
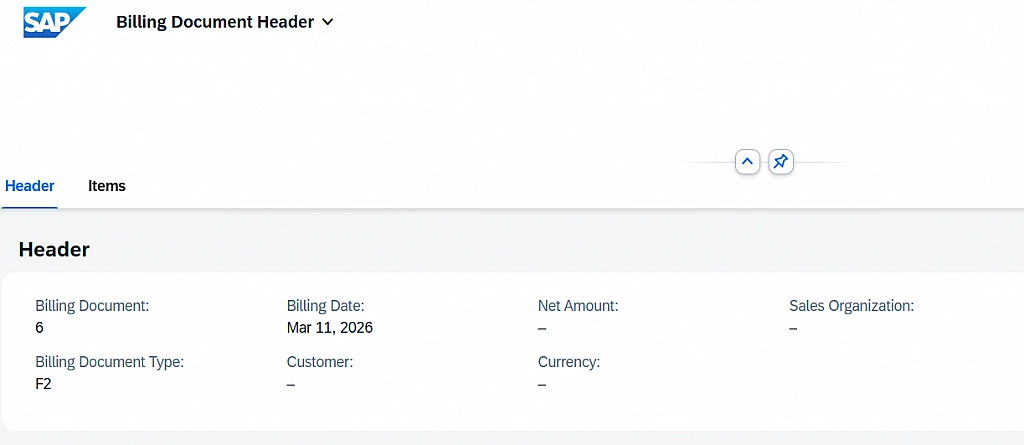
After execution, a new billing document record is created successfully.
Thanks for reading.